Python Control Statement
Python Basics
Python Introduction
Python Installation
Overview of Jupyter IDE
Identifiers & Reserved Keywords
Python Variables
Python Numbers
Python Operators
Python Operators and Arithmetic Operators
Comparison and Logical Operators
Assignment and Bitwise Operators
Identity and Membership Operators
Python Flow Control
if else if else statement
While Loop Statement
Python For Loop
Break and Continue Statement
Python Data Types
Python Strings
Python Strings Methods
Python Lists
Python Tuples
Python Dictionary
Python Functions
Introduction to Python Functions
Function Arguments
Recursion Function
Lambda/Anonymous Function
Python - Modules
Python Files
Python - Files I/O
Python - Exceptions Handling
Python - Debugging
Python Indentation
Sample JAVA Program
Python Control Statements
It is used in Python for decision making.It is required when we want to execute a code only if a certain condition is satisfied.
Python is having 4 types of control statement
- if
- if else
- if elif else
- nested if
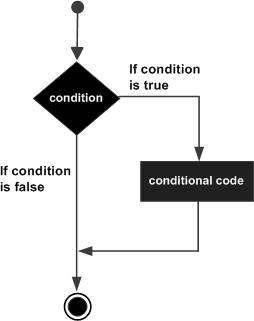
1. if statement
Note: Python interprets non-zero values as True. None and 0 are interpreted as False.
Syntax:
if test expression:
statement(s) ( Tab or 4 white space)
Example
# Program to check whether the user age is below 18 or not
user_age = 15
if(user_age <= 18):
print("User age is 18 or younger")
Output:
User age is 18 or younger
# Program to check whether the user age is below 18 or not
user_age = 20 # Execute twice with both the conditions
if(user_age <= 18):
print("User age is 18 or younger")
print("This line will be executed always")
Output:
This line will be executed always
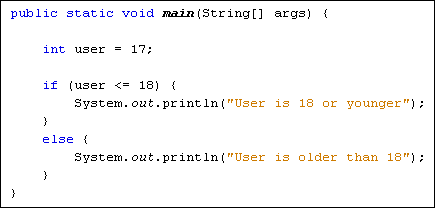
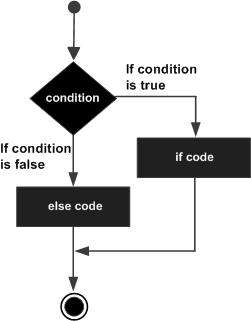
2. if ... else Statement
Syntax:
if test expression:
Body of if "statement(s)" ( Tab or 4 white space)
else:
Body of else "statement(s)" ( Tab or 4 white space)
Example
# Program to check whether the user age is below 18 or not
user_age = 22
if(user_age <= 18):
print("User age is 18 or younger")
else:
print("User age is above 18")
Output:
User age is above 18
# Program to verify whether the number is positive or not
num = 10 # Execute twice with negative value
if num > 0:
print("Positive number")
else:
print("Negative Number")
Output:
Positive number
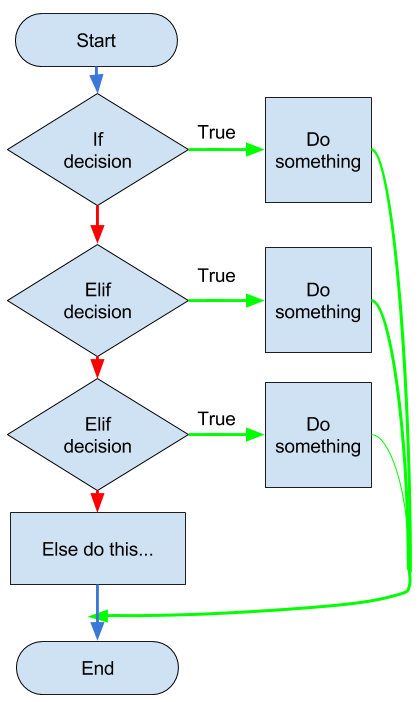
3. if...elif...else Statement
Note: The if block can have only one else block. But it can have multiple elif blocks.
Syntax:
if test expression:
Body of if "statement(s)" ( Tab or 4 white space)
elif test expression:
Body of elif "statement(s)" ( Tab or 4 white space)
else:
Body of else "statement(s)" ( Tab or 4 white space)
Example:
# Program to verify whether the number is positive or not
num = 0
if num > 0:
print("Positive number")
elif num == 0:
print("ZERO")
else:
print("Negative Number")
Output:
ZERO
# Program to verify total number of digits
num = 100
if 9 < num < 99:
print("Two digit number")
elif 99 < num < 999:
print("Three digit number")
elif 999 < num < 9999:
print("Four digit number")
else:
print("Number is not in the mentioned range")
Output:
Three digit number
Note: Python does not provide switch or case statements as in other languages, but we can use if..elif...statements to simulate switch
# Program to display the month name
month_num = 12
if month_num == 1:
print("January Month")
elif month_num == 2:
print("February Month")
elif month_num == 3:
print("March Month")
elif month_num == 4:
print("April Month")
elif month_num == 5:
print("May Month")
elif month_num == 6:
print("June Month")
elif month_num == 7:
print("July Month")
elif month_num == 8:
print("August Month")
elif month_num == 9:
print("September Month")
elif month_num == 10:
print("October Month")
elif month_num == 11:
print("November Month")
elif month_num == 12:
print("December Month")
else:
print("Enter a valid number")
Output:
December Month
4. Nested if Statements
Note: Any number of these statements can be nested inside one another. Indentation is the only way to figure out the level of nesting. This can get confusing, so must be avoided if we can
Syntax:
if expression1:
statement(s)
if expression2: # Nested if
statement(s)
elif expression3:
statement(s)
elif expression4:
statement(s)
else:
statement(s)
else:
statement(s)
Example:
# Program to verify whether the number is positive or not
num = 20
if num >= 0:
if num == 0:
print("Zero")
else:
print("Positive number")
else:
print("Negative number")
Output:
Positive number
