Python Operators and Arithmetic Operators
Python Basics
Python Introduction
Python Installation
Overview of Jupyter IDE
Identifiers & Reserved Keywords
Python Variables
Python Numbers
Python Operators
Python Operators and Arithmetic Operators
Comparison and Logical Operators
Assignment and Bitwise Operators
Identity and Membership Operators
Python Flow Control
if else if else statement
While Loop Statement
Python For Loop
Break and Continue Statement
Python Data Types
Python Strings
Python Strings Methods
Python Lists
Python Tuples
Python Dictionary
Python Functions
Introduction to Python Functions
Function Arguments
Recursion Function
Lambda/Anonymous Function
Python - Modules
Python Files
Python - Files I/O
Python - Exceptions Handling
Python - Debugging
What are Operators in Python?
Operators are special symbols in Python that carry out arithmetic or logical computation. The value that the operator operates on is called the operand.
Example :
10 + 5 = 15.
Here, + is the operator that performs addition. 10 and 5 are the operands and 15 is the output of the operation.
Types of Operator
Python language supports the following types of operators.
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison (Relational) Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Membership Operators
- Identity Operators
Let us have a look on all operators one by one.
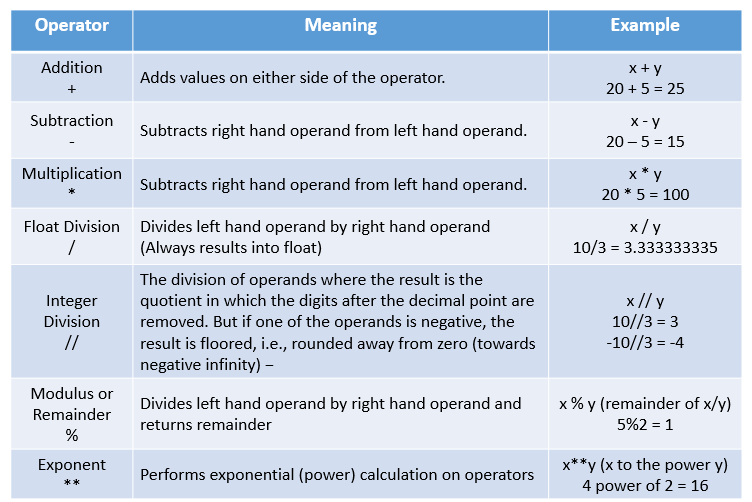
Arthimetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used to perform mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication etc.
#Sample Code
a = 10
b = 20
print(a+b)
print('Sum of two numbers',a+b)
print('Sum of {1} + {1} + {1} ='.format(a,b),a+b)
Output:
30
Sum of two numbers 30
Sum of 20 + 20 + 20 = 30
# Sample Code
x = 20
y = 5
# Addition Operator
print('Addition of {} + {} ='.format(x,y),x+y)
# Subtraction Operator
print('Subtraction of {} - {} ='.format(x,y),x-y)
# Multiplication Operator
print('Multiplication of {} * {} ='.format(x,y),x*y)
Output:
Addition of 20 + 5 = 25
Subtraction of 20 - 5 = 15
Multiplication of 20 * 5 = 100
Note: While multiplying Integer and Float value, the result will be a float value.
#Sample Code j= 3 * 1.5 print(j) print(type(j)) Output: 4.5 class 'float'
# Sample Code
x = 10
y = 3
# Float Division Operator
print('Float Division of {} / {} ='.format(x,y),x/y)
# Integer Division Operator
print('Integer Division of {} // {} ='.format(x,y),x//y)
# Integer Division for Negative Value
print('Integer Division of Negative Numbers =',-10//3)
Output:
Float Division of 10 / 3 = 3.3333333333333335
Integer Division of 10 // 3 = 3
Integer Division of Negative Numbers = -4
# Modulus or Remainder Operator
x = 5
y = 2
print('Modulus of {} % {} ='.format(x,y),x%y)
Output:
Modulus of 5 % 2 = 1
# Exponentiation Operator
x = 4
y = 2
print('Exponentiation of {} raise to the power {} ='.format(x,y),x**y)
Output:
Exponentiation of 4 raise to the power 2 = 16
Rule of Precedence in Python
Below table guides the order in which operation are carried out.
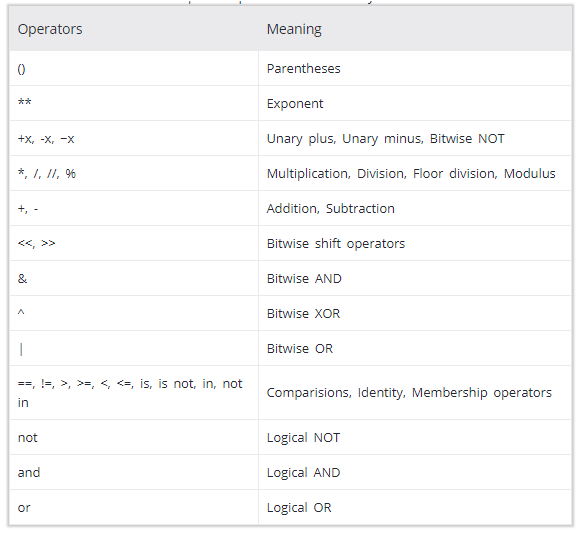
# Exponent followed by Subraction 12 - 5 * 2 Output: 2
# Parenthesis followed by Multiplication (12 - 5) * 2 Output: 14
