Python List
Python Basics
Python Introduction
Python Installation
Overview of Jupyter IDE
Identifiers & Reserved Keywords
Python Variables
Python Numbers
Python Operators
Python Operators and Arithmetic Operators
Comparison and Logical Operators
Assignment and Bitwise Operators
Identity and Membership Operators
Python Flow Control
if else if else statement
While Loop Statement
Python For Loop
Break and Continue Statement
Python Data Types
Python Strings
Python Strings Methods
Python Lists
Python Tuples
Python Dictionary
Python Functions
Introduction to Python Functions
Function Arguments
Recursion Function
Lambda/Anonymous Function
Python - Modules
Python Files
Python - Files I/O
Python - Exceptions Handling
Python - Debugging
What is Lists ?
Eg: list1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Creating list in python
# Create an empty list list1 = [] print(list1) #list of integers list2 = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] print(list2) # list of strings list3 = ["Python","Java","C"] print(list3) # list of lists list4 = [[15, 25], ["Python","Data Science"]] print(list4) # list of different datatypes list5 = [50, 98.3,'Python', [15, 25] ] print(list5) Output: [] [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] ['Python', 'Java', 'C'] [[15, 25], ['Python', 'Data Science']] [50, 98.3, 'Python', [15, 25]]
List Indexing and Slicing
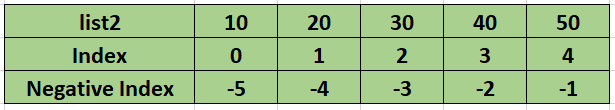
Negative Indexing
Sample Code
#list of integers list2 = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] #print second element print(list2[2]) #print last element using negative index print(list2[-2]) #slicing from index 1 to index 3 print(list2[1:3]) # Other ways of slicing - Use it as per the requirement print(list2[:]) print(list2[1:]) print(list2[:3]) Output: 30 40 [20, 30] [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] [20, 30, 40, 50] [10, 20, 30]
Updating Lists
# Sample Code
list3 = ["Python","Java","C"]
print("List Before Updating the item",list3)
list3[2] = "R"
print("List after Updating the item",list3)
Output:
List Before Updating the item ['Python', 'Java', 'C']
List after Updating the item ['Python', 'Java', 'R']
Delete List Elements
To remove a list element, you can use the del statement if you know exactly which element(s) you are deleting
#Sample Code #del to remove item based on index position list3 = ["Python","Java","C"] del list3[0] print(list3) # Delete a particular item (or) #del list3 #print(list3) # Delete the full list Output: ['Java', 'C']
Traversing List using for loop
#loop through a List
Month = ["Jan","Feb","Mar","Apr","May","June","July","Aug","Sep","Oct","Nov","Dec"]
for element in Month:
print(element)
Output:
Jan
Feb
Mar
Apr
May
June
July
Aug
Sep
Oct
Nov
Dec
List Methods
1. Concatenation
# "+" - It Concatenates two list, List1 and List2 List1 = ["Vinoth","Anand","Kumaran"] List2 = ["Sathish","Vignesh"] FinalList = List1 + List2 print(List1) print(List2) print(FinalList) Output: ['Vinoth', 'Anand', 'Kumaran'] ['Sathish', 'Vignesh'] ['Vinoth', 'Anand', 'Kumaran', 'Sathish', 'Vignesh']
2. Length
# Length of sequence, i.e. the number of elements in the list.
List1 = [2,4,5,6,7,8,9,12,34,56,78,45,67,45,86,222]
print("length of the list is",len(List1))
Output:
length of the list is 16
3. Repetition
# n copies of list concatenated List1 = ["Python"] print(List1 * 7) Output: ['Python', 'Python', 'Python', 'Python', 'Python', 'Python', 'Python']
4. Membership
# Sample Code for 'in' operator - True if element x is in list. list1 = [26, 34, 24, 61, 132] print(24 in list1) # Sample Code for 'not in' operator -True if element x is not in list. print(35 not in list1) Output: True True
5. Smallest number in the list
# Smallest element in list.
list1 = [26, 34, 24, 61, 132]
print("The smallest number in the list is",min(list1))
Output:
The smallest number in the list is 24
6. Largest number in the list
#Largest element in list.
list1 = [26, 34, 24, 61, 132]
print("The largest number in the list is",max(list1))
Output:
The largest number in the list is 132
7. Sum of all the numbers in the list
# Sum of all numbers in list
List1 = [2,4,5,6,7,8,9,12,34,56,78,45,67,45,86,222]
print("Sum of all the numbers in the list is",sum(List1))
Output:
Sum of all the numbers in the list is 686
8. Append
# It Adds an element x to the end of the list and returns None.
#Appending the element
List1 = ["Vinoth","Anand","Kumaran"]
List1.append("Sathish")
print(List1)
#Appending the list
List2 = ["Raghul", "Santhosh"]
List1.append(List2)
print(List1)
Output:
['Vinoth', 'Anand', 'Kumaran', 'Sathish']
['Vinoth', 'Anand', 'Kumaran', 'Sathish', ['Raghul', 'Santhosh']]
9. Extend
# Appends all the elements from one list to the another list and returns None. List1 = ["Vinoth","Anand","Kumaran","Sathish"] List2 = ["Raghul","Santhosh"] List1.extend(List2) print(List1) Output: ['Vinoth', 'Anand', 'Kumaran', 'Sathish', 'Raghul', 'Santhosh']
10. Insert
# Inserts an element x at a given index. # Note: The first element in the list has index 0 and returns None.. list1 = [1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9,10] list1.insert(4,5) # Location , Value as arguments print(list1) List2 = ["Vinoth","Anand","Kumaran","Sathish"] List2.insert(2,"Vignesh") print(List2) Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] ['Vinoth', 'Anand', 'Vignesh', 'Kumaran', 'Sathish']
11. Remove
# Removes the first occurrence of element x from the list and returns None
list1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,4]
list1.remove(4) # it will remove first occurence of '4' in a given list
print(list1)
List2 = ["Vinoth","Anand","Kumaran","Sathish"]
List2.remove("Anand")
print(List2)
Output:
[1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 4]
['Vinoth', 'Kumaran', 'Sathish']
12. Pop
# Removes the element at the given position and returns it. The parameter i is optional.
# If it is not specified, pop() removes and returns the last element in the list.
list1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
a = list1.pop()
print("The value removed is",a)
print(list1)
List2 = ["Vinoth","Anand","Kumaran","Sathish"]
a = List2.pop(2)
print("The value removed is",a)
print(List2)
Output:
The value removed is 10
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
The value removed is Kumaran
['Vinoth', 'Anand', 'Sathish']
13. Count
# Returns the number of times element x appears in the list. numbers = [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2] print(numbers.count(1)) Output: 3
14. Reverse
#Reverse the list and returns None list1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] list1.reverse() print(list1) List2 = ["Vinoth","Anand","Kumaran","Sathish"] List2.reverse() print(List2) Output: [10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1] ['Sathish', 'Kumaran', 'Anand', 'Vinoth']
15. Sort
# vowels list
vowels = ['e', 'a', 'u', 'o', 'i']
# sort the vowels
vowels.sort()
# print vowels
print('Sorted list:', vowels)
Output:
Sorted list: ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u']
# Setting reverse=True sorts the list in the descending order
# vowels list
vowels = ['e', 'a', 'u', 'o', 'i']
# sort the vowels
vowels.sort(reverse=True)
# print vowels
print('Sorted list (in Descending):', vowels)
Output:
Sorted list (in Descending): ['u', 'o', 'i', 'e', 'a']
# Numbers
list1 = [99, 19, 4, 1, 54, 25, 2]
# sort the vowels
list1.sort()
# print vowels
print('Sorted list:', list1)
Output:
Sorted list: [1, 2, 4, 19, 25, 54, 99]
String Split to create a list
split() method breaks up a string at the specified separator and returns a list of strings.
# splits at space
str1= 'Welcome to Python Class'
print(str1.split())
str2 = "Vinoth,Anand,Santhosh,Raghul"
# splits at ','
print(str2.split(','))
# splits at ':'
str3 = "121212121:1212121:21434322434:4234234"
print(str3.split(':'))
Output:
['Welcome', 'to', 'Python', 'Class']
['Vinoth', 'Anand', 'Santhosh', 'Raghul']
['121212121', '1212121', '21434322434', '4234234']
List Comprehensions
# Without list comprehension
cube = []
for i in range(10):
cube.append(i**3)
print(cube)
Output:
[0, 1, 8, 27, 64, 125, 216, 343, 512, 729]
#Using list comprehension cube = [i**3 for i in range(10)] print(cube) Output: [0, 1, 8, 27, 64, 125, 216, 343, 512, 729]
# Print the Even Numbers
list1 = [ x for x in range(20) if x % 2 == 0 ]
print("The Even numbers in the list are",list1)
# Print the Odd Numbers
list2 = [ x for x in range(20) if x % 2 != 0 ]
print("The Odd numbers in the list are",list2)
Output:
The Even numbers in the list are [0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18]
The Odd numbers in the list are [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19]
