Python For Loop Statement
Python Basics
Python Introduction
Python Installation
Overview of Jupyter IDE
Identifiers & Reserved Keywords
Python Variables
Python Numbers
Python Operators
Python Operators and Arithmetic Operators
Comparison and Logical Operators
Assignment and Bitwise Operators
Identity and Membership Operators
Python Flow Control
if else if else statement
While Loop Statement
Python For Loop
Break and Continue Statement
Python Data Types
Python Strings
Python Strings Methods
Python Lists
Python Tuples
Python Dictionary
Python Functions
Introduction to Python Functions
Function Arguments
Recursion Function
Lambda/Anonymous Function
Python - Modules
Python Files
Python - Files I/O
Python - Exceptions Handling
Python - Debugging
Python Loops
A loop statement allows us to execute a statement or group of statements multiple times.
Python has two primitive loop commands:
For Loop
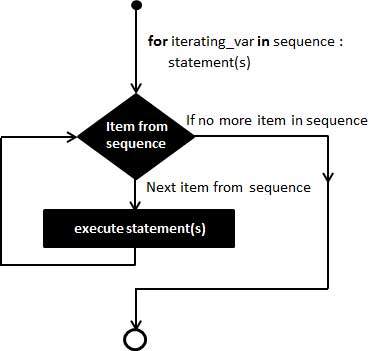
Syntax:
for iterating_var in sequence:
statements(s)
# Program to print the fruits available inside the list
fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Cherry","Mango","Pineapple","Jackfruit"]
for x in fruits:
print(x)
Output:
Apple
Banana
Cherry
Mango
Pineapple
Jackfruit
# Program to print the numbers available inside the list
numbers = [0, 1, 5, 10, 15, 45, 50]
for i in numbers:
print(i)
Output:
0
1
5
10
15
45
50
Using else Statement with Loops
If the else statement is used with a for loop, the else statement is executed when the loop has exhausted iterating the list.
# Program to print the numbers available inside the list using else statement
numbers = [0, 1, 5, 10, 15, 45, 50]
for i in numbers:
print(i)
else:
print("No items left")
Output:
0
1
5
10
15
45
50
No items left
# Program to find the sum of all numbers stored in a list
# List of numbers
numbers = [0, 1, 5, 10, 15, 45, 50]
# variable to store the sum
sum = 0
# iterate over the list
for val in numbers:
sum = sum + val
print("The sum of numbers in the list is", sum)
Output:
The sum of numbers in the list is 126
Looping Through a String
# Program to print each character of a string
for x in "banana":
print(x)
Output:
b
a
n
a
n
a
The range() function
# Program to generate 10 numbers starting from 0 to 9 using Range Function print(range(10)) Output: range(0, 10)
# Program to display the numbers using Range Function
for x in range(10):
print(x)
Output:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# Program to display the numbers between 2 values using Range Function
for x in range(2,6):
print(x)
Output:
2
3
4
5
# Program to display the numbers between 2 values using step size
for x in range(1, 30, 2):
print(x)
Output:
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
21
23
25
27
29
Iterating by Sequence Index
An alternative way of iterating through each item is by index offset into the sequence itself.
# Program to iterate through a list using indexing
fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Cherry","Mango","Pineapple","Jackfruit"]
for index in range(len(fruits)):
print ('Fruit name is :', fruits[index])
Output:
Fruit name is : Apple
Fruit name is : Banana
Fruit name is : Cherry
Fruit name is : Mango
Fruit name is : Pineapple
Fruit name is : Jackfruit
# A list of fruits fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Cherry","Mango","Pineapple","Jackfruit"] ## Read fruits list and enumerate into index and value # Enumerate() method adds a counter to an iterable and
returns it in a form of enumerate object. for index,value in enumerate(fruits): print(index,value) # print ('Fruit Index is',index,'and Fruit name is :',value) Output: 0 Apple 1 Banana 2 Cherry 3 Mango 4 Pineapple 5 Jackfruit
Nested For Loop
Python programming language allows to use one for loop inside another for loop.
# Nested for loop example
for x in range(1,4): # 1 ,2, 3
### Inner for loop ###
for y in range(1,4):
print(x,y)
Output:
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
2 2
2 3
3 1
3 2
3 3
# Nested for loop example
adj = ["red", "big", "tasty"]
fruits = ["apple", "mango", "banana"]
for x in adj:
for y in fruits:
print(x, y)
Output:
red apple
red mango
red banana
big apple
big mango
big banana
tasty apple
tasty mango
tasty banana
