Identity and Membership Operators
Python Basics
Python Introduction
Python Installation
Overview of Jupyter IDE
Identifiers & Reserved Keywords
Python Variables
Python Numbers
Python Operators
Python Operators and Arithmetic Operators
Comparison and Logical Operators
Assignment and Bitwise Operators
Identity and Membership Operators
Python Flow Control
if else if else statement
While Loop Statement
Python For Loop
Break and Continue Statement
Python Data Types
Python Strings
Python Strings Methods
Python Lists
Python Tuples
Python Dictionary
Python Functions
Introduction to Python Functions
Function Arguments
Recursion Function
Lambda/Anonymous Function
Python - Modules
Python Files
Python - Files I/O
Python - Exceptions Handling
Python - Debugging
Special Operators
Python language offers some special type of operators like the identity operator or the membership operator. They are described below with examples.
Identity Operators
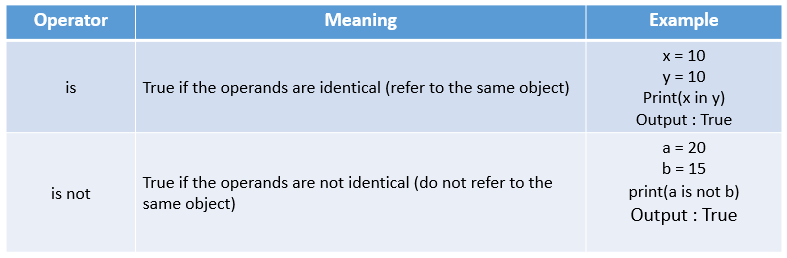
Note: For understanding purpose retriving id details (i.e) memory allocation. But in real time you can directly use 'is' operator. No need to verify the memory address.
# Example 1 - Numbers using 'is' operator
x = 10
print("memory location of x is",id(x))
y = 10
print("memory location of y is",id(y))
print (x is y) #10 is object created once both x and y points to same object
Output:
memory location of x is 140708939362336
memory location of y is 140708939362336
True
# Example 2 - String using 'is' operator
a = "Python"
print("memory location of a is",id(a))
b = "Python"
print("memory location of b is",id(b))
# "Python" is object created once both a and b points to same object
print (a is b)
Output:
memory location of a is 2332982898792
memory location of b is 2332982898792
True
# Example 3 - List using 'is' operator
l1 = [1,2,3,4]
print("memory location of l1 is",id(l1))
l2 = [1,2,3,4]
print("memory location of l2 is",id(l2))
print (l1 is l2) # list l1 and l1 will create a separate objects
Output:
memory location of l1 is 2333051991112
memory location of l2 is 2333042340296
False
# Example 4 - Numbers using 'is not' operator x = 10 y = 10 print (x is not y) a = 20 b = 15 print(a is not b) Output: False True
# Example 5 - String using 'is not' operator s1 = "Python" s2 = "Python" print (s1 is not s2) s3 = "Python" s4 = "Java" print (s3 is not s4) Output: False True
# Example 6 - List using 'is' operator l1 = [1,2,3,4] l2 = [1,2,3,4] print (l1 is not l2) Output: True
Conclusion:
'is' operator will display true if the memory address is same and
'is not' operator will display true if the memory address is different.
Membership Operators
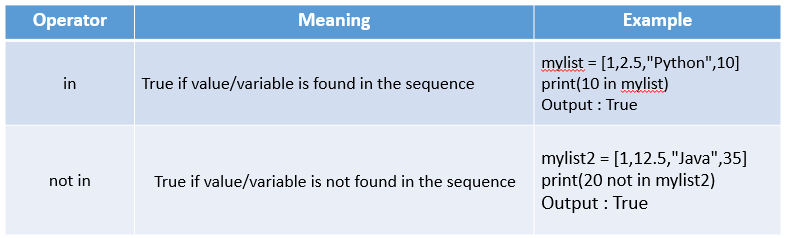
# Example 1 - List using 'in' operator
mylist = [1,2.5,"Python",10]
print(10 in mylist)
print("Python" in mylist)
print(5 in mylist)
Output:
True
True
False
# Example 2 - List using 'not in' operator
mylist2 = [1,12.5,"Java",35]
print(10 not in mylist2)
print("Java" not in mylist2)
Output:
True
False
Conclusion:
'in' operator will display true if the value is found in the sequence and
'not in' operator will display true if the value is not found in the sequence.
